The Properties of Water Video Handout Answer Key provides a comprehensive overview of the unique characteristics and significance of water. This guide delves into the physical, chemical, and biological properties of water, exploring their practical applications and environmental implications.
From its unique density and polarity to its crucial role in biological processes, this handout offers a thorough understanding of water’s multifaceted nature and its profound impact on our world.
Properties of Water Video Handout Answer Key: Basic Overview
The Properties of Water Video Handout Answer Key provides a comprehensive summary of the key concepts discussed in the accompanying video handout. It is intended for students and individuals seeking a deeper understanding of the unique properties of water and their implications in various contexts.
Physical Properties of Water
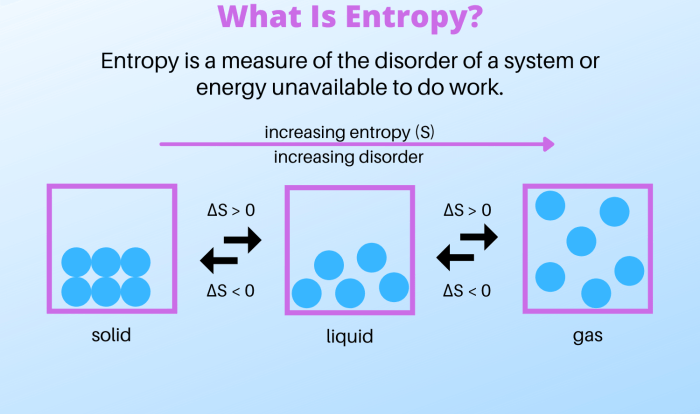
Water exhibits several distinctive physical properties that contribute to its unique behavior. Its density, for instance, is higher than that of most other liquids, allowing it to sink in denser fluids. Water also has a high boiling point and a relatively low freezing point compared to other substances of similar molecular weight, which makes it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Chemical Properties of Water
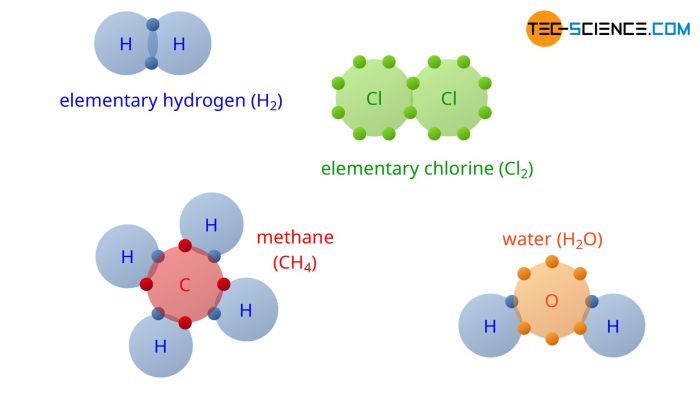
Water’s chemical composition is H 2O, consisting of two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to an oxygen atom. The polarity of water molecules, with a slight positive charge on the hydrogen atoms and a slight negative charge on the oxygen atom, enables water to form hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules.
Biological Importance of Water
Water is essential for life and plays a crucial role in various biological processes. It serves as a solvent for biochemical reactions, facilitates the transport of nutrients and waste products, and provides a medium for cellular metabolism. Water’s high specific heat capacity allows it to absorb and release large amounts of heat without significant temperature changes, contributing to temperature regulation in organisms.
Applications of Water’s Properties, Properties of water video handout answer key
The unique properties of water have led to its widespread use in various fields. In science, water is employed as a solvent, a coolant, and a reaction medium. In industry, it is utilized in processes such as manufacturing, food processing, and power generation.
In everyday life, water is indispensable for drinking, cooking, cleaning, and irrigation.
Environmental Significance of Water
Water is a vital component of the Earth’s ecosystems and plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. It supports aquatic life, regulates the climate, and shapes landscapes through erosion and deposition. Human activities, such as pollution and overconsumption, pose threats to water resources, emphasizing the need for conservation and sustainable water management practices.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Cohesion: The attraction between water molecules due to hydrogen bonding, which gives water its surface tension and capillary action.
Adhesion: The attraction between water molecules and other substances, such as glass or soil, which contributes to water’s ability to wet surfaces.
Surface tension: The force that causes the surface of water to behave like a stretched elastic membrane, giving rise to phenomena like water droplets and capillary waves.
Clarifying Questions
What is the density of water?
At room temperature (20°C), the density of water is approximately 1 gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
Why is water a polar molecule?
Water is a polar molecule due to the uneven distribution of electrons within its molecular structure, resulting in a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other.
How does water’s polarity affect its behavior?
The polarity of water molecules enables them to form hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules, which influences their interactions with substances and their behavior in various contexts.