The accounting cycle includes all of the following except – The accounting cycle, a fundamental process in the financial world, encompasses a sequence of steps that transform raw financial data into meaningful financial statements. While most discussions focus on the entirety of the cycle, this exploration delves into the exceptions, examining what the accounting cycle notably excludes.
Throughout this discussion, we will unravel the intricacies of the accounting cycle, highlighting its crucial components and shedding light on the specific steps that fall outside its scope. By delving into these exceptions, we gain a deeper understanding of the accounting process and its limitations.
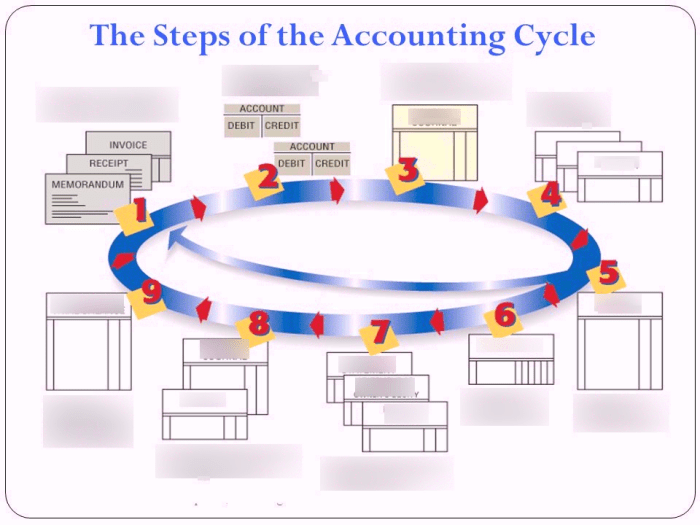
1. The Accounting Cycle Steps
The accounting cycle is a comprehensive process that involves recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions to provide information about a company’s financial performance and position. It consists of a series of sequential steps that ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial statements.
Steps Involved in the Accounting Cycle:
- Recording transactions in a journal
- Posting transactions to the ledger
- Preparing a trial balance
- Adjusting entries
- Preparing an adjusted trial balance
- Preparing financial statements
- Closing entries
- Preparing a post-closing trial balance
Each step in the accounting cycle plays a vital role in ensuring the accuracy and completeness of financial information.
2. Financial Statements
Financial statements are formal reports that provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance and position. They are used by various stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and management, to make informed decisions.
Types of Financial Statements:
- Balance sheet
- Income statement
- Statement of cash flows
- Statement of changes in equity
Each financial statement provides specific information about a company’s financial health, such as its assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses, and cash flows.
3. Transactions and their Impact
Accounting transactions are economic events that affect a company’s financial position. They are recorded in the accounting system to provide a complete record of the company’s financial activities.
Types of Transactions:
- Cash transactions
- Non-cash transactions
- Revenue transactions
- Expense transactions
- Asset transactions
- Liability transactions
- Equity transactions
Transactions impact financial statements by affecting the balances of various accounts. For example, a cash sale will increase cash and revenue.
4. Accounting Equation: The Accounting Cycle Includes All Of The Following Except
The accounting equation is a fundamental principle of accounting that states that the total assets of a company must equal the sum of its liabilities and equity. This equation provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time.
Accounting Equation:, The accounting cycle includes all of the following except
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
The accounting equation is used throughout the accounting cycle to ensure the accuracy and completeness of financial information.
5. Adjusting Entries

Adjusting entries are journal entries made at the end of an accounting period to correct for errors and omissions in the initial recording of transactions. They ensure that the financial statements reflect the true financial position of the company.
Purpose of Adjusting Entries:
- To record accrued revenues
- To record accrued expenses
- To record depreciation and amortization
- To adjust for inventory shrinkage
Adjusting entries are essential for the accuracy and reliability of financial statements.
6. Closing Entries

Closing entries are journal entries made at the end of an accounting period to transfer temporary account balances to permanent accounts. This process resets the temporary accounts for the next accounting period.
Purpose of Closing Entries:
- To close revenue and expense accounts
- To close gain and loss accounts
- To update the retained earnings account
Closing entries are necessary to prepare the financial statements and ensure the continuity of the accounting system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of the accounting cycle?
The accounting cycle serves as the backbone of financial reporting, providing a systematic approach to recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions to generate accurate and reliable financial statements.
Can the accounting cycle be modified to accommodate specific industry requirements?
Yes, the accounting cycle can be adapted to meet the unique needs of different industries. Certain industries may require additional steps or specialized accounting practices that fall outside the standard cycle.
What are some examples of steps that may be excluded from the accounting cycle?
Steps related to specialized accounting practices, such as consolidation of financial statements for parent companies and subsidiaries, or industry-specific calculations, such as those required for insurance companies, may be excluded from the standard accounting cycle.