Welcome to the fascinating world of rock pocket mouse lab answers, where we delve into the intriguing adaptations and behaviors of this desert-dwelling rodent. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of this resilient creature, exploring its unique characteristics and the groundbreaking discoveries made through laboratory studies.
From its remarkable physical adaptations to its intricate social behaviors, the rock pocket mouse has captivated scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. Through meticulous laboratory studies, researchers have gained invaluable insights into the strategies this animal employs to survive and thrive in its challenging environment.
Rock Pocket Mouse
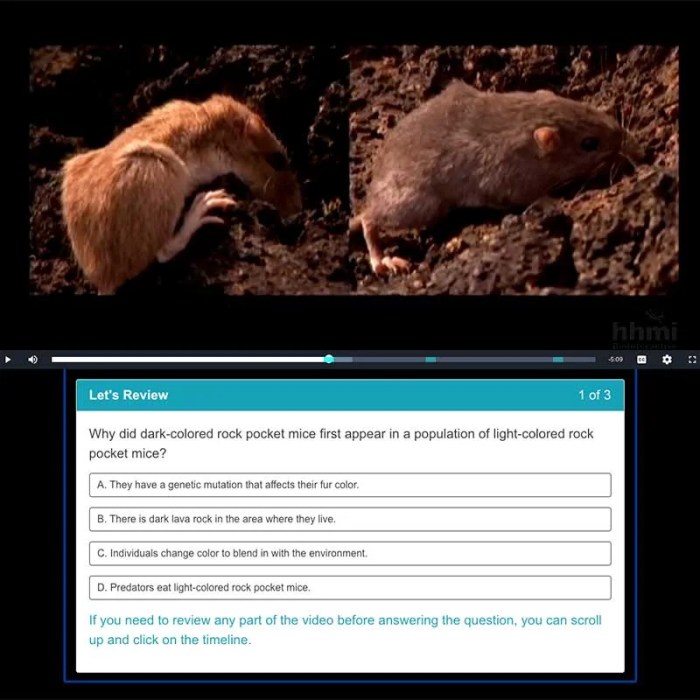
The rock pocket mouse is a small rodent that lives in rocky habitats throughout the western United States. It is distinguished by its large eyes, long tail, and pale brown fur. Rock pocket mice are well-adapted to their rocky environment, with strong claws and teeth for climbing and chewing.
They are also able to store food in their cheek pouches, which helps them to survive during periods of food scarcity.
Habitat and Ecological Niche
Rock pocket mice are found in rocky habitats, including deserts, canyons, and mountains. They typically live in crevices or under rocks, where they find shelter from predators and the elements. Rock pocket mice are omnivores, and their diet consists of seeds, insects, and small vertebrates.
They are also known to eat the leaves and stems of certain plants.
Conservation Status and Threats, Rock pocket mouse lab answers
Rock pocket mice are currently listed as a species of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). However, their populations are threatened by habitat loss and fragmentation. As human development encroaches on their natural habitat, rock pocket mice are forced to live in smaller and more isolated areas.
This can lead to increased competition for resources and a decline in genetic diversity.
Laboratory Studies
Laboratory studies on rock pocket mice have been conducted to investigate various aspects of their biology, behavior, and ecology. These studies have employed diverse methodologies and techniques, including behavioral observations, physiological measurements, and genetic analyses.
Behavioral observations have been used to study the social interactions, mating systems, and foraging strategies of rock pocket mice. Physiological measurements have provided insights into their thermoregulation, water balance, and energy metabolism. Genetic analyses have helped elucidate their evolutionary history and genetic diversity.
Significant Findings
Laboratory studies on rock pocket mice have yielded significant findings that have contributed to our understanding of this species. For instance, behavioral studies have revealed that rock pocket mice exhibit complex social behaviors, including cooperative breeding and alloparental care. Physiological studies have shown that they have remarkable adaptations for surviving in arid environments, such as the ability to concentrate urine and tolerate high temperatures.
Genetic studies have provided evidence for the genetic distinctiveness of rock pocket mice and have helped identify the genetic basis of some of their unique traits. These studies have also shed light on the evolutionary relationships between rock pocket mice and other species in the genus Perognathus.
If you’re looking for the answers to your rock pocket mouse lab, you might want to take a break and delve into the adventures of Don Quixote in Chapter 3. Follow the valiant knight’s hilarious mishaps and misinterpretations in Don Quixote Summary Chapter 3 . After you’ve had a good chuckle, come back and conquer those rock pocket mouse lab answers with newfound vigor!
Behavioral Adaptations

Rock pocket mice exhibit a suite of social and behavioral adaptations that contribute to their survival and success in their rocky, arid environments. These adaptations include group living, cooperative behaviors, and anti-predator strategies.
Group living is a common feature of rock pocket mice populations. Mice live in social groups of up to 20 individuals, with a dominant male and female pair at the core. Group living provides several benefits to individual mice, including increased access to food and shelter, enhanced predator detection and avoidance, and reduced energy expenditure for thermoregulation.
Cooperative behaviors are also evident in rock pocket mice. For example, mice will often huddle together to conserve body heat during cold nights. They will also share food and resources with other group members, and will even care for the young of other mice in the group.
Rock pocket mice have also evolved a number of anti-predator strategies. These include camouflage, crypsis, and escape behaviors. Camouflage and crypsis help mice to avoid detection by predators, while escape behaviors allow them to evade predators if they are detected.
The social and behavioral adaptations of rock pocket mice are essential for their survival and success in their challenging environment. These adaptations allow mice to exploit the resources of their habitat, avoid predators, and reproduce successfully.
Group Living
- Enhanced access to food and shelter
- Improved predator detection and avoidance
- Reduced energy expenditure for thermoregulation
Cooperative Behaviors
- Huddling for warmth
- Sharing food and resources
- Caring for the young of others
Anti-Predator Strategies
- Camouflage and crypsis
- Escape behaviors
Physiological Adaptations
Rock pocket mice have evolved remarkable physiological adaptations that enable them to thrive in their arid and rocky habitats. These adaptations include water conservation mechanisms, temperature regulation strategies, and energy-efficient metabolic processes.
Water Conservation
Water scarcity is a significant challenge in the desert ecosystem. Rock pocket mice have developed several adaptations to minimize water loss and maximize water utilization.
- Concentrated Urine:Their kidneys produce highly concentrated urine, reducing water loss through excretion.
- Water-Efficient Metabolism:They have a low metabolic rate, which minimizes water production as a byproduct of metabolism.
- Behavioral Adaptations:They minimize water loss through behavioral adaptations such as avoiding daytime activities and seeking shelter in burrows to reduce evaporation.
Temperature Regulation
Extreme temperature fluctuations are common in desert habitats. Rock pocket mice have evolved strategies to maintain their body temperature within a narrow range.
- Torpor:They enter a state of torpor during extreme cold or heat, reducing their metabolic rate and body temperature to conserve energy.
- Burrowing:They utilize burrows for shelter, which provide insulation from extreme temperatures.
- Large Ears:Their large ears have a high surface area, allowing for efficient heat dissipation in hot conditions.
Energy Efficiency
Energy conservation is crucial for survival in resource-limited habitats. Rock pocket mice have evolved adaptations to maximize energy utilization.
- Low Metabolic Rate:They have a low basal metabolic rate, conserving energy when food resources are scarce.
- Fat Storage:They store fat reserves in their tails, providing an energy source during periods of food shortage.
- Efficient Digestion:Their digestive system has adapted to extract maximum nutrients from the limited vegetation available in their habitat.
Captivity and Research: Rock Pocket Mouse Lab Answers
Rock pocket mice have emerged as crucial subjects in scientific research, shedding light on diverse aspects of biology and ecology. Captive studies have provided valuable insights into their behavior, physiology, and adaptations, advancing our understanding of this remarkable species.
Importance of Captive Research
Captive research enables researchers to conduct controlled experiments, isolate variables, and observe animals under specific conditions. This allows for precise measurements and detailed analysis of behaviors and physiological responses that may be challenging to study in the wild. Captive environments also provide a safe and controlled setting for long-term monitoring and data collection.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Studying animals in captivity poses ethical challenges that must be carefully considered. Researchers have a responsibility to ensure the well-being and welfare of the animals under their care. This includes providing adequate housing, nutrition, and veterinary care. Additionally, it is crucial to minimize stress and ensure that research methods do not cause unnecessary harm or distress.
Contributions to Rock Pocket Mouse Biology and Conservation
Captive research has significantly contributed to our understanding of rock pocket mouse biology. Studies have examined their reproductive behavior, dietary preferences, social interactions, and physiological adaptations. This knowledge has aided in developing conservation strategies and identifying potential threats to their populations.
Furthermore, captive breeding programs have played a vital role in the conservation of endangered rock pocket mouse subspecies. These programs help maintain genetic diversity and provide a source of individuals for reintroduction efforts, ensuring the survival of these unique and ecologically important species.
General Inquiries
What is the significance of rock pocket mouse lab answers?
Rock pocket mouse lab answers provide valuable insights into the adaptations, behaviors, and ecological roles of this desert-dwelling rodent. They contribute to our understanding of species conservation and the preservation of fragile ecosystems.
How do laboratory studies help us understand rock pocket mice?
Laboratory studies allow researchers to observe and manipulate environmental conditions, enabling them to study specific aspects of rock pocket mouse behavior, physiology, and adaptations. These studies provide controlled environments for testing hypotheses and gaining insights into the animal’s unique characteristics.
What are some ethical considerations associated with studying rock pocket mice in captivity?
Researchers must prioritize the well-being of rock pocket mice in captivity, ensuring they receive proper care, nutrition, and a suitable environment. Ethical considerations include minimizing stress, providing adequate space, and respecting the animals’ natural behaviors.